In the world of digital product development, "it works on my machine" is no longer the benchmark for success. As developers and businesses sourcing premium scripts from Fileev, the ultimate goal is to build systems that can grow from ten users to ten million without breaking.
Scalability isn't just about adding more servers; it’s about architectural foresight. In this guide, we will dissect the layers of modern web development, from the frontend framework to the database indexing strategies that keep your application snappy.
Choosing the Right Foundation: Monolith vs. Microservices
Before writing a single line of code, you must decide on the structural philosophy of your application.
The Monolithic Approach
For many startups and independent creators on Fileev, a Monolith is the most efficient starting point. In a monolith, the frontend, backend, and database logic are all contained within a single codebase.
Pros: Simplified testing, easy deployment, and low latency between components.
Cons: As the app grows, the codebase becomes a "big ball of mud," making it hard to update specific features without risking the whole system.
The Microservices Revolution
If you are building an enterprise-level tool—such as a multi-vendor marketplace or a high-traffic SaaS—Microservices are the answer. Here, you break the app into independent services (e.g., Auth Service, Payment Service, Product Service) that communicate via APIs.
Pros: Independent scaling, technology flexibility (use Python for AI and Go for performance), and fault isolation.
Cons: High operational complexity and the "fallacy of distributed computing" (network latency).
Frontend Excellence: Beyond Basic HTML
The frontend is the "face" of your Fileev digital asset. To ensure it remains performant under load, we must look at Rendering Strategies.
Client-Side Rendering (CSR)
Popularized by React and Vue, CSR shifts the work to the user's browser. While this creates a "fluid" app-like feel, it can hurt SEO and initial load times.
Server-Side Rendering (SSR) and Static Site Generation (SSG)
For content-heavy platforms, tools like Next.js or Nuxt.js are essential.
SSR generates the HTML on every request, providing fresh data and excellent SEO.
SSG builds the pages at build-time. If you are selling digital templates or blog posts, SSG offers unmatched speed because the server simply serves a pre-rendered file.
The Data Layer: SQL vs. NoSQL
One of the most frequent technical debates on CodeCraft Insights is which database to use. The answer depends entirely on your data's relationship.
Relational Databases (PostgreSQL, MySQL)
If your data is structured and requires complex relationships (like a user having many orders, and orders having many products), SQL is king.
Pro Tip: Use PostgreSQL for its advanced features like JSONB support, which allows you to store semi-structured data within a strictly typed relational system.
Non-Relational Databases (MongoDB, Redis)
When dealing with rapidly changing data structures or the need for extreme horizontal scaling, NoSQL shines. Redis, specifically, is an essential tool for Caching. By storing frequently accessed data in-memory, you can reduce database load by up to 80%.
The Power of API Design: REST vs. GraphQL
How your frontend communicates with your backend determines the developer experience (DX).
REST (Representational State Transfer)
The industry standard. It’s predictable and leverages standard HTTP methods ($GET, POST, PUT, DELETE$). However, REST often suffers from "over-fetching" (receiving more data than you need).
GraphQL
Developed by Facebook, GraphQL allows the client to request exactly what it needs. If you only need a user's name and profile picture, you ask for just that. This is incredibly powerful for mobile apps where bandwidth is a concern.
Infrastructure and DevOps: The "Silent" Backbone
A great script from Fileev needs a great home. Modern deployment has moved away from manual FTP uploads to CI/CD (Continuous Integration / Continuous Deployment).
Containerization with Docker
Docker allows you to package your application and all its dependencies into a "container." This ensures that the environment on your local machine is identical to the production server. No more “dependency hell.”
Orchestration with Kubernetes
When you have dozens of microservices, managing them manually is impossible. Kubernetes automates the scaling, management, and deployment of your containers.
Security Best Practices for Digital Assets
Security is not a feature; it is a requirement. When implementing technical solutions, follow these pillars:
Sanitize All Inputs: Prevent SQL Injection and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS).
Use HTTPS Everywhere: Protect data in transit with SSL/TLS certificates.
JWT for Auth: Use JSON Web Tokens for stateless authentication in distributed systems.
Rate Limiting: Protect your APIs from brute-force attacks and DDoS.
Performance Optimization: The 1-Second Rule
Studies show that users begin to drop off if a page takes more than 2 seconds to load. To stay under the "1-second rule," implement:
CDN (Content Delivery Network): Serve images and scripts from servers physically close to the user.
Lazy Loading: Only load images and components when they enter the user's viewport.
Minification: Compress your CSS and JavaScript files to reduce their payload size.
Integrating Fileev Assets into the Ecosystem
When you purchase a script or template from Fileev, you aren't just buying code; you're buying a building block. To integrate these effectively:
Read the Documentation: Every premium asset has specific environmental requirements.
Refactor for Scalability: If a script uses a local file system for storage, consider switching it to an S3 Bucket (like Amazon S3 or DigitalOcean Spaces) for better scale.
Monitor: Use tools like Sentry or LogRocket to track errors in real-time after deployment.
Conclusion: The Ever-Evolving Tech Landscape
The technical world moves fast. Today's "shining" language (as mentioned in our previous posts) might be tomorrow's legacy code. However, the fundamental principles of clean architecture, security, and scalability remain constant.
By focusing on these core pillars, you ensure that your digital products—whether built from scratch or accelerated by Fileev assets—are robust, professional, and ready for the future.
Technical Deep Dive: Calculating Throughput
For those looking at the math of scaling, consider the basic formula for system capacity:
$$Throughput = \frac{Concurrent Users \times Requests Per User}{Average Response Time}$$
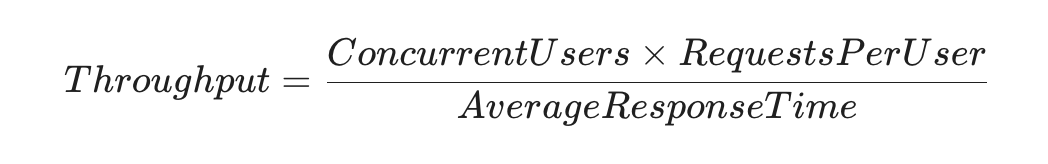
Reducing your response time by even 100ms can significantly increase the number of concurrent users your server can handle without additional hardware costs.

Comments (0)